RGD motif in SCGF
Integrin-binding motif RGD peptide is present in bony fish SCGF, but not in cartilaginous fish, amphibian and reptile SCGF. Every mammal is divided into two groups according to SCGF with or without RGD peptide as shown in the Table below. Most mammals have RGD+ SCGF, while mice, rats, squirrels, rabbits, horses and marsupial mammals have RGD- SCGF. Seemingly random species variation of mammalian RGD+ and RGD- SCGF is explicitly based on phylogenetic animal evolution (see Figure below, red box: RGD+ SCGF, blue box: RGD- SCGF).
Bats are primary host harboring SARS-CoV-2 with RGD+ spike protein mutated from RGD- SARS-CoV-1 (
666). SARS-CoV-2 invades into target cells by binding to their integrin α5β1 through RGD peptide of spike protein (
667,
668). Bats have RGD+ SCGF, and some have SCGF with 2 RGD peptides (listed in the Table). SARS-Cov-2-infected bats are asymptomatic, possibly because RGD+ SCGF competes with SARS-CoV-2 spike protein through RGD peptide for binding to integrin α5β1 of target cells and resultantly inhibits viral invasion into cells. SCGF can be one of defensive factors in innate immunity.
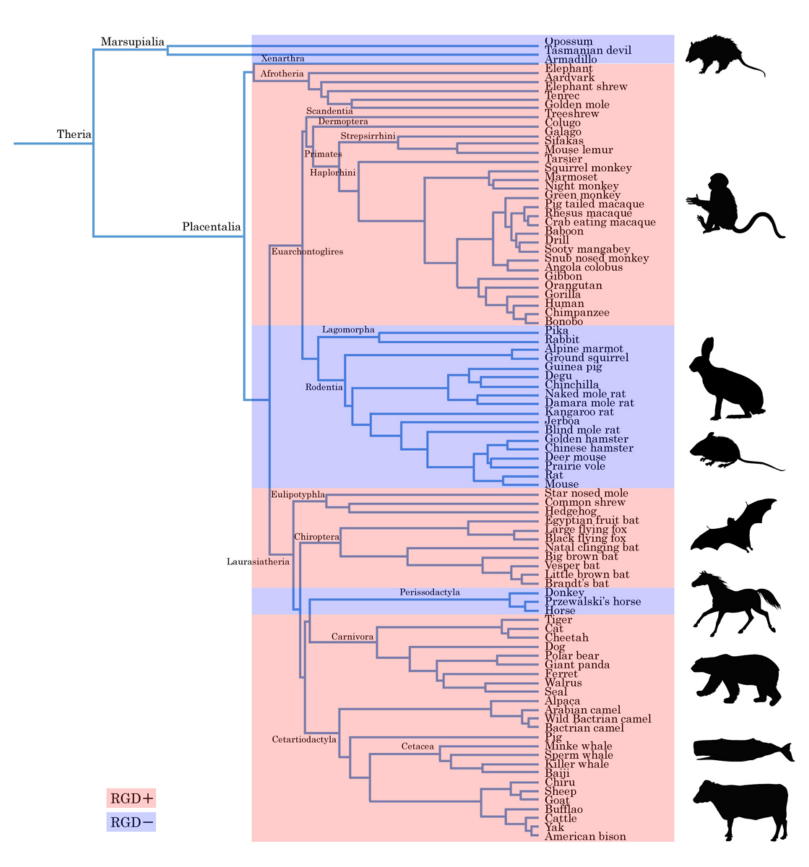
(modified from
Curr. Biol. 27:3025-3033, 2017, illustrated by Creazilla)
|
RGD |
+ |
- |
Mammal |
Human
Monkey
Chimpanzee, Gorilla, Orangutan, Bonobo, Gibbon,
Cynomolgus monkey, Baboon, Rhesus monkey,
Marmoset
Deer
Dog
Cat
Tiger, Lion, Cheetah, Wildcat
Cattle (Cow)
Elephant
Goat, Sheep
Pig, Boar
Bear, Giant panda
Fox
Hyena
Sloth
Mustela
Otter, Ferret, Mink, Stoat, Badger
Beaver
Mongoose, Meerkat
Hedgehog
Tenrec
Whale, Orca, Dolphin, Seal, Sea lion, Narwhal
Pangolin
Bat |
Mouse, Rat, Vole, Hamster, Guinea pig, Blesmol
Squirrel
Pika
Horse
Donkey
Camel
Wombat
Opossum
Koala
Tasmanian devil
Brushtail possum
Aardvark
Platypus |
Reptile |
|
Snake
Crocodile
Lizard
Turtle |
Amphibian |
Western clawed frog |
Frog |
Fish |
Bony fish
Salmon, Tuna, Flounder, Herring, Medaka, Eel,
Catfish |
Bony fish
Lungfish, Coelacanth, Arowana
Cartilaginous fish
Shark |
Bat SCGF |
1 RGD |
2 RGDs |
Pteropus vampyrus (Large flying fox)
Molossus molossus (Pallas's mastiff bat)
Rhinolophus ferrumequinum (Greater horseshoe bat)
Eptesicus fuscus (Big brown bat)
Rousettus aegyptiacus (Egyptian rousette)
Pipistrellus kuhlii (Kuhl's pipistrelle)
Myotis myotis (Whiskered bat) |
Phyllostomus hastatus (Greater spear-nosed bat)
Phyllostomus discolor (Pale spear-nosed bat)
Desmodus rotundus (Common vampire bat)
Artibeus jamaicensis (Jamaican fruit-eating bat) |
Vertebrate
scgf cDNA has been accumulated in
GenBank database.
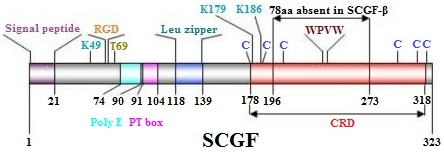
An isolated human
scgf cDNA consists of 972 nucleotides encoding 323 aa (hSCGF-α) (
7). The full-length hSCGF is characterized with (1) conserved Ca
2+-dependent carbohydrate-recognition domain (CRD) consensus motif 110-130 aa sequence [
C-[LIVMFATG]-x(5,12)-[WL]-x-[DNSR]-x(2)-C-x(5,6)-[FYWLIVSTA]-[LIVSTA]-C] at COOH-terminal; 4
Cysteines (C) involved in two disulfide bonds, 5
tryptophans (W) and
VDYV, containing a
WPVW motif for attachment of a mannosyl residue to tryptophan, (2)
78 aa (A196-G273) absent in hSCGF-β,
(3) 21 aa
signal sequence, (4)
RGDsequence of a cell adhesion motif, (5)
poly-glutamic acidic region, (6) Pro/Ser/Thr-rich
PT box,(7)xleucine zipper(13), (8)
T69 for N-acetylgalactosamine O-glycosylation (
433), and (9)
K49(
434),
K179(
435) and
K186(
435,
436) for ubiquitination.
 Among the members of C-type lectin
family, hSCGF shows the highest
homology with tetranectin (TN), a
plasminogen kringle 4-binding protein.
hSCGF shows 32.2%, 27.2% and 33.7%aa identity, and 48.0%, 46.5% and 53.6%aa similarity to hTN (8), mTN (9) and
shark TN (10), respectively.
Among the members of C-type lectin
family, hSCGF shows the highest
homology with tetranectin (TN), a
plasminogen kringle 4-binding protein.
hSCGF shows 32.2%, 27.2% and 33.7%aa identity, and 48.0%, 46.5% and 53.6%aa similarity to hTN (8), mTN (9) and
shark TN (10), respectively. TN but not SCGF has K-X-E-X
14-D aa motif in the CRD for binding to plasminogen kringle-4 (
571).
Phylogenetic tree of the C-type lectin family is shown
above (click to enlarge the image).